What Is Data Management and How It Applies to Your Business

In the last five years, the global market value of business-generated customer data has doubled– jumping from $12.3 million in 2017 to $24.7 million in 2022. Today’s businesses generate and collect more data than ever before, and that data continues to accrue in potential value. The growth of customer and operational data presents businesses of all sizes with challenges and opportunities. For those who would seize this opportunity, success begins with data management.
While the global market value of data continues to rise, strategic data management for most businesses remains a fragmented process scattered across multiple unintegrated platforms. In ad hoc processes, businesses store customer and operational data on partitioned databases containing widespread redundancies and inconsistencies. The average number of data sources in regular use in marketing alone has doubled since 2020.
For most businesses, managing and integrating data from disparate sources limits their ability to leverage data effectively for improved decision-making. Past integrating uncommunicative data sources remains the problem of sorting good data from bad. Bad corporate data takes an annual toll of $3.1 trillion on the US economy alone.
In this guide, you’ll learn what data management is and how to apply it effectively in your business.
Key Takeaways:
- Data management is a broad term encompassing practices that treat data as a valuable resource to leverage in decision-making processes.
- Businesses large and small generate more data now than ever before. With or without a process to manage it, that data has significant potential value for business performance
- Businesses at any stage of digital transformation can adopt data management practices that will deliver superior, actionable insights.
What Is Data Management?
Data management refers to the collection of disciplines or practices that treat data as a valuable resource. These disciplines, among others, include:
- Data Governance
- Data Warehousing
- Data Quality
- Data Storage and Database Management
Effective data management is a critical component of establishing IT systems that run business applications and provide analytical data to enable corporate executives, business managers, and other decision-makers to make informed operational decisions.
The data management process involves multiple practices that work together to ensure that data in business systems is correct, accessible, and available. Although IT and data management teams handle most of the work, other team members throughout departments also contribute to various aspects of the processes to ensure that the data fulfills their needs.
5 Data Management Applications for Your Business
Whether you’ve had a data management plan in place for years or have just been winging it, several inter-industry best practices can improve data management in any organization. Here’s a list of five concepts you can begin applying today.
1. Assess Your Current Data Intake and Storage Processes
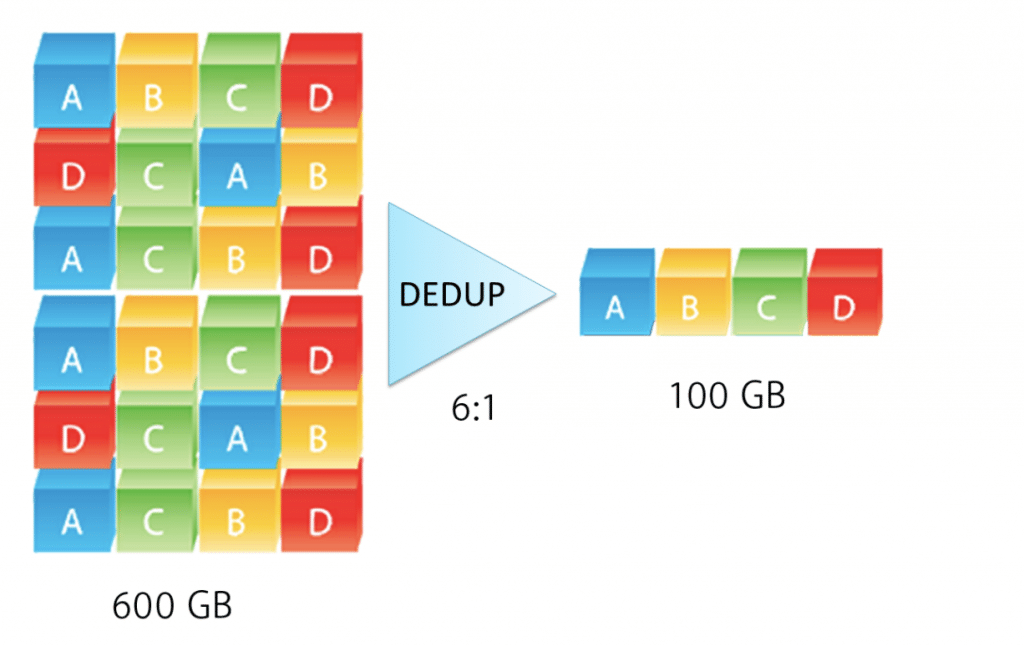
Depending on the applications you already use, your business likely replicates multiple unnecessary data instances. In increasingly cloud-based workloads, data replication to a certain degree can be an asset, mitigating the risk of catastrophic data loss. Nevertheless, as systems compound account-based and transactional data instances, your storage costs bloat needlessly. Systematic deduplication of data can reduce storage costs by 20-40%.
2. Establish Data Protection and Security Standards
Data breaches are on the rise, jumping 68% in 2021. Protecting your customer data and honoring customer privacy protects your business’ image and reputation. It also mitigates significant legal liabilities in a period of accelerated cybercrime. In the EU, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) stipulates harsh consequences for businesses that fail to observe data privacy standards. While no such comprehensive legislation currently exists in the US, recent posturing by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the FTC express an increasingly broad intent to treat customer data privacy and security as a matter of public safety.
3. Develop Data Visualization Techniques
Data collection alone does not suffice to create value at the bottom line. Data needs to be packaged and presented in mediums that communicate persuasive, actionable insights to decision-makers of varying skill sets and backgrounds.
When analysts present in the boardroom, they need a medium of expression that speaks to everyone. In any environment, two-thirds of people are visual learners who receive the impact of statistical or numerical data in visual formats much more persuasively than as raw numbers or statements. Data visualization formats include:
- Tables
- Charts
- Graphs
- Maps
- Timelines
- Matrices
- Scatterplots
- Word clouds
4. Maintain Standards of Data Quality
Data only delivers value and actionable insights if reliable and internally consistent. Across organizations, bad data appears to be endemic, affecting 88% of companies at the bottom line and costing the average enterprise $15 million annually. In unintegrated systems with multiple redundancies, bad data appears in varying forms.
- Missing Records: Databases may show conflicting numbers of customer accounts owing to data entry discrepancies.
- Duplicate Records: Insufficient validations may allow multiple entries for the same account, keyed to different identifiers such as name, email, or phone number.
- Incomplete Records: Your data may contain unvalidated entries lacking critical components.
- Obsolete Data: Databases not configured for regular, timely updates will contain a significant amount of outdated information that can skew your analytics.
5. Invest in Data Management Tools
Managing digital assets and documents can challenge even the most tech-savvy organizations. Businesses large and small benefit from having a single source of truth that all team members can access at their touchpoints. Depending on the nature of your business, the data management tools appropriate to your needs may be an Integration-Platform-as-a-Service (IPaaS) that connects cloud-based services, processes, and applications in a single interface. In other contexts, simple organizational tools such as document management software suffice to create data clarity.
Out-of-the-Box Comprehensive Document Management with FileCenter
For businesses of all sizes and industries, FileCenter offers the most fully-featured and affordable document management software on the market. FileCenter’s document management solution combines easy scanning and file organization with powerful PDF creation and editing.
To download a free trial, visit FileCenter today.


