The Quick Guide to Document Storage in the Cloud
Business is moving to the cloud. By the end of 2022, more than half of global organizations – 56% – will run at least 50% of their workloads in the cloud. While data breaches continue to concern decision-makers, long-term scalability, reduced operating costs, and unrivaled protection against catastrophic data loss have made cloud document storage a permanent feature of the modern workplace.
As businesses continue to adopt remote work as a permanent practice, three out of four executives now want to enable remote access for company files. Cloud storage reliably lowers operating costs while allowing real-time collaborative work from anywhere, on any device. The cloud migration that began during temporary Covid-19 restrictions has acquired lasting momentum and will soon become the standard operating practice for most businesses.
In this quick guide, you’ll learn about the cloud, what it is, and what the benefits of cloud document storage are.
Key Takeaways:
- Cloud document storage is a method of data storage in which documents and files are stored remotely on a network of servers managed by a cloud hosting service.
- Because companies only pay for the storage they use, cloud storage lowers operating costs compared to local storage systems.
- Cloud storage enables remote access, improves collaboration, and can protect against catastrophic data loss.
What is Cloud Document Storage?
The cloud refers to software and storage services that users access via the internet rather than physically local devices. Cloud service providers operate networks of servers that deliver on-demand computing and storage capabilities. The physical location of cloud servers operated by cloud hosting companies is unimportant to the services they provide.
Cloud service providers take responsibility for maintaining their servers and ensuring that clients have access to their stored assets. Service providers also manage all physical infrastructure. Clients pay only for the storage and computing services they use, allowing businesses to accurately align operating costs with needs.
There are three kinds of cloud storage architectures.
- Object Storage: Objects can contain large volumes of unstructured data such as photos and videos.
- File Storage: File systems thoroughly index stored data in nested hierarchies of filenames and directories. Data in file systems can be easily searched and retrieved even in granular quantities.
- Block Storage: Data blocking arranges stored data into sequences of fixed byte-length called blocks.
While object and block storage outperform file storage systems in the amount of data they can store in a given quantity of server space, file storage does not require new code to work with document management applications. File storage also contains the locking and sharing mechanisms necessary to preserve up-to-date file versions.
With document management software, administrators can set permissions for documents stored in cloud filing systems so that multiple users can create and edit documents with detailed version histories and master copies.
Cloud Storage Security Concerns
Cloud storage of company documents and records comes with certain risks that decision-makers should evaluate in the context of their specific circumstances. For 75% of businesses, cloud security issues remain a top concern.

1. Data Breaches
Cloud storage of sensitive information increases the total number of remote access points as well the number of people who may maliciously or inadvertently share credentials. With introduced risks for misconfigurations and unauthorized access, cloud storage effectively expands the cybercrime attack surface of your sensitive information.
2. Long-Term Viability of Cloud Service Providers
Information stored in the cloud is only as resilient to disruption as the service provider. As with any other business type, cloud service businesses may fail or file for bankruptcy. Businesses need to consider the long-term viability of their cloud service partners.
3. Performance
Outsourced data storage may perform at lower speeds than local storage. Depending on bandwidth limitations and how much data needs to regularly accessed, cloud storage may adversely affect some business operations.
6 Benefits of Cloud Document Storage
Migrating document storage to the cloud can provide several advantages over local storage.
1. Remote Accessibility
Cloud storage gives authorized users access to their documents anytime and anywhere. Remote accessibility speeds up communication and breakdown bottlenecks in document-related workflows.
2. Scalability
Cloud storage allows you to pay for only the storage capacity you need. When you run your own local servers, accurately anticipating the scale of your storage needs with enough time to procure and install new hardware can prove challenging. With cloud storage, you can scale your storage capacity up or down at any time as your needs dictate.
3. Synchronization
Cloud storage platforms allow users to sync devices so that the files they access always represent current canonical versions. Synchronization can prevent versioning disparities and keep everyone on the same page.
4. Reduced Energy Consumption
Many public cloud data centers operate with energy efficiencies well above industry averages. In the European Union, companies migrating to cloud storage and applications have experienced 80% reductions in total energy consumption and cut carbon emissions by 96%.
5. Disaster Recovery
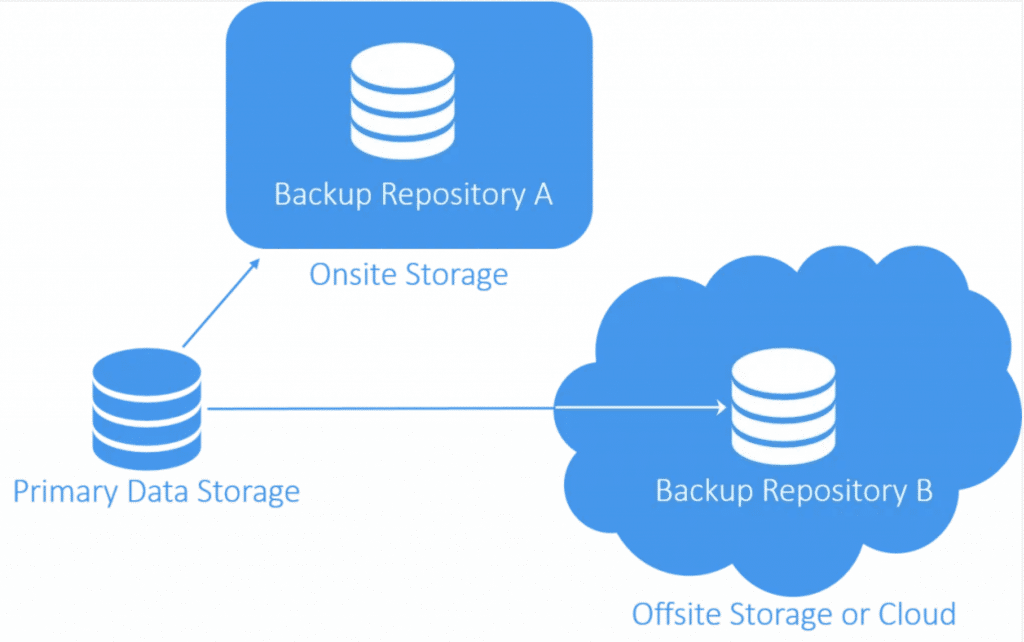
Storing documents and other important digital assets in the cloud provides the most secure disaster recovery plan. This includes not just natural disasters that may destroy facilities but also ransomware attacks that encrypt your data. Most cloud storage providers practice data redundancy with options for archiving and keep data stored in multiple physical locations, making catastrophic data a near impossibility.
6. Lower Storage and Computing Thresholds for Devices
Cloud storage and cloud-based applications make it possible for users to access and work with documents on a broader range of devices. Desktop processing power isn’t necessary to work in cloud environments and users can work with lighter devices such as phones and tablets.
Manage Your Documents in the Cloud with FileCenter
With an intuitive filing system, enabled PDF editing, and internal search capabilities, FileCenter offers the most fully featured and affordable document management solutions available today. FileCenter’s Document Management software works seamlessly with SharePoint, Google Drive, OneDrive, DropBox, and other popular cloud services.
To download a free trial or schedule a demo, visit FileCenter today.


